In late March last year, as the virus started to spread across India, investors began to worry about the impact a potential pandemic could have on their portfolio firms.
They exchanged notes, and on April 1, penned a joint open letter to the local startup ecosystem, advising firms to “prepare for the worst.”
In the months that followed, the virus engulfed the South Asian market and, among other things, hit the brakes on funding activity. Scrambling to steer through the unprecedented event, startups began to cut expenses. Some didn’t survive, and a few got acquired in fire sales. Many entrepreneurs and investors stepped up and volunteered to help the nation fight the pandemic, too.
Investors were right about the impact the virus would have on the country, and by extension, on the firms attempting to fuel the economy. But very few were prepared for what was about to happen in just a few quarters.
Scores of startups, many operating in edtech and fintech categories, began to report fast growth. “We started to see three years and five years of growth in one year,” said Ashish Dave, chief executive of Mirae Asset Venture’s India business.
While several investors, including many tier 1 funds that are generally very active in India, were still cautious, a group of investors including Tiger Global, Falcon Edge Capital, and SoftBank shifted into a higher gear.
Navroz Udwadia of Alpha Wave Global (formerly known as Falcon Edge Capital) said in a conference earlier this year that his firm likes to get aggressive when most other funds are cautious about the market conditions.
Tiger Global backed Infra.Market in February this year, propelling the business-to-business e-commerce platform’s valuation from $200 million to over $1 billion in a span of two months.
In a letter to investors in February, Tiger Global said the opportunity it sees in areas such as consumer, enterprise, and financial technology in the U.S., China, and India is “very large relative to the amount of capital we manage and evolving at a rate that is often hard to comprehend.”
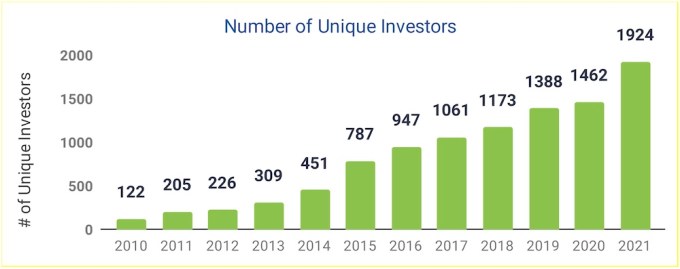
Several factors worked in India’s favor, many investors said. There’s an abundance of dry powder in the market and investors are increasingly looking at growth avenues such as emerging regions as their next big bets. It also helped that Beijing enforced a series of crackdowns on its own startups and made it difficult for foreign money to flow into China.
Another thing swinging in favor of India was the record number of IPOs that we saw this year. Food delivery firm Zomato made a stellar debut. Fashion commerce Nykaa, online insurer PolicyBazaar also made strong debuts on the stock exchanges. Paytm filed for the nation’s largest IPO, though the public market is still giving it less valuation than it sought.
Dave said Indian startups going public addressed the exit challenge that many investors have faced over the years.
The investors’ bullishness on India was on full display in April, when the virus was beginning to gain pace again in the country.
Eight Indian startups — including social commerce Meesho, fintech CRED, investment platform Groww, business-to-business messaging platform Gupshup, payments firm Chargebee — joined the unicorn club in April. Tiger minted five of these unicorns.
The sudden flow of cash also created a crunch for talent in the market. Startups began to offer lucrative stock options and salary hikes to employees to win and retain them.
In total, capital flowing to private Indian startups surged over four times to about $39 billion this year and nearly three times from the previous best of $14.6 billion in 2019, according to data from insight platform Tracxn, which has also filed for an IPO.
India now has 81 unicorns, 44 of which joined the club this year. Several of the unicorns and many other fast growing startups have raised multiple rounds this year and increased their valuations multiple times over. Fintech Slice, which is giving millions of Indians access to credit card features and helping them build credit scores, increased its valuation multiple-fold in a recent round it raised from Insight Partners and Tiger Global.
CRED, for instance, has raised three funding rounds and has held talks for a fourth one, TechCrunch reported earlier. Indian edtech giant Byju’s has raised over $1.5 billion since last year. Instant grocery delivery startup Zepto, co-founded by two 19-year-old Stanford dropouts, doubled its valuation to $570 million in a span of two months.
Fintech startup Jar, which is helping hundreds of thousands of Indians start their investment journey, is about to close a round from a high-profile investor, said two people familiar with the matter. The startup, founded this year, is likely to increase its valuation by about 15 times in the new round.
Bangalore-based QuestBook, which is helping developers transition to web3, is about to close a round from a number of investors including entrepreneur Balaji Srinivasan, according to a person familiar with the matter. Polygon is in talks to raise from Sequoia Capital India and Steadview Capital, TechCrunch reported this month. (Also Amazon is in talks to back an agritech startup, per two people familiar with the matter.)
“Startups have become mainstream in India,” said Dave, pointing to a number of recent developments including the arrival of Shark Tank in the country. “Indian parents are no longer hesitant to tell their friends that their kid works at a startup or has founded one. Everyone now knows what a startup is. For years, I had to explain to my dad what I do for a living!”
Tiger Global, which has made over 50 investments in India this year, is currently conducting due diligence to back an additional nine startups in the country, according to a person familiar with the matter. Other than Tiger Global, SoftBank, and Alpha Wave Global have also deployed serious capital in the country this year. SoftBank has invested over $3 billion in India this year. Alpha Wave Global has poured over $2 billion.
The frenetic pace at which some of these firms have written checks to Indian startups this year has also forced many of their global peers to take India more seriously. Temasek, which typically backs late stage startups, has made a record 20 investments in India this year.
Insight Partners, which became more prolific in India this year, made some changes to its investment process in the country to speed up the time it takes to back a startup, two people familiar with the matter said. It’s currently engaging to back Indian NFT platform Faze, according to two people with knowledge of those proceedings.
General Catalyst is building a team in India, too. The firm is also in talks to back a number of startups including OneCode, a person familiar with the matter said. Andreessen Horowitz made its first investment in India this year. B Capital Group has also appointed a new India head.
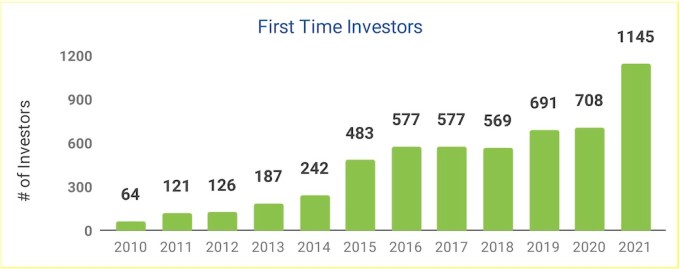
“Tiger has changed the game,” said Dave. “Every fund on the planet has at some point relooked and reassessed their strategy and tried to figure out what is the best they can do. Not everyone can play Tiger’s game. But what is the next best you can do? Because you can’t play the same game that you used to.”
Sequoia Capital India, which has been investing in India for over a decade, remains the most prolific investor in India and Southeast Asia. It has made over 60 investments this year.
Dave said he expects the pace of investments to continue in the new year. “The market will continue to become more competitive. Just look at the number of people who are beginning to do angel investing.”
“Overseas, the market is huge. The number of investors and firms are also very large. That’s still not the case in India. So the competition for good deals is very high.”
